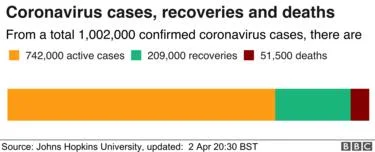
More than a million cases of coronavirus have been registered globally, according to the latest figures from Johns Hopkins University – another grim milestone as the world grapples with the spreading pandemic.
More than 51,000 people have died and more than 208,000 have recovered, according to the university’s figures.
The US accounts for the most cases; Italy the highest death toll.
The disease, Covid-19, first emerged in central China three months ago.
Though the tally kept by Johns Hopkins records one million confirmed cases, the actual number is thought to be much higher.
It took a month and a half for the first 100,000 cases to be registered. A million was reached after a doubling in cases over the past week.
Nearly a quarter of cases have been registered in the United States, while Europe accounts for around half.
What’s the latest?
On Thursday, Spain said 950 people had died in the previous 24 hours – thought to be the highest number of deaths of any country in one day.
The number of confirmed Spanish cases rose from 102,136 on Wednesday to 110,238 – an 8% rise that is similar to the rate recorded in previous days.
Authorities believe the virus is now peaking and say they expect to see a drop in figures in the days ahead.
“We continue with an increase of around 8%. This points, as we have already seen, to a stabilisation in the data that we’re registering,” María José Sierra, from the Spanish health ministry’s emergency co-ordination unit, said at a news conference.
Spain, the second-worst hit nation in terms of deaths, has also lost nearly 900,000 jobs.
The US on Thursday said it saw a record 6.6 million new unemployment benefit claims.
How did we get here?
In China at the end of December, 34-year-old ophthalmologist Dr Li Wenliang tried to send a message to other medics warning them about a new virus in Wuhan, in Hubei Province.
He was later visited by the police accused of scaremongering.
On 3 January we wrote our first news report about a “mystery virus” in Wuhan. At the time, 44 cases had been confirmed, 11 of which were considered severe.
There had been no deaths yet, but many feared we would see a repeat of the 2003 Sars outbreak that killed 774 people. By 18 January the confirmed number of cases had risen to around 60 – but experts estimated the real figure was closer to 1,700.
Just two days later, as millions of people prepared to travel for the lunar new year, the number of cases more than tripled to more than 200 and the virus was detected in Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen.
On 23 January, Wuhan went into lockdown. At that point, 18 people had died – 17 in Hubei, and one in Beijing – and 570 others had been infected, including in Taiwan, Japan, Thailand, South Korea and the United States.
Ten days later, a 44-year-old man in the Philippines died of the virus – the first death reported outside of China.
On 6 February Dr Li Wenliang himself succumbed to the virus.
A week later, an 80-year-old tourist died in France – Europe’s first coronavirus death. The virus appeared in Iran five days later – two people died within hours of their diagnosis being announced. Iran would later become a hotspot for the virus.
Italy saw a major surge in cases on 23 February, and 10 towns in Lombardy went into lockdown. On 10 March the lockdown was extended to the whole of Italy.
On 23 March, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced a three-week lockdown in the UK.
Three days later, on 26 March, the US officially overtook China as the country hardest-hit by the coronavirus outbreak, with more than 86,000 confirmed cases. By 2 April, this had risen to more than 217,000 – almost double the number of cases in Italy.
BBC




2 Comments